3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that creates solid objects from digital models by depositing layers of material on top of each other. 3D printing has many applications in various fields, such as aerospace, biomedical, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Titanium Alloy is one of the most widely used materials for 3D printing. It has high strength, low density, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Especially Ti-6Al-4V is one of the most commonly used materials, widely used in aerospace areas.

Currently, a lot of research is focused on how to deoxidize and remanufacture used titanium powders and scrap into powders that are suitable for 3D printing.
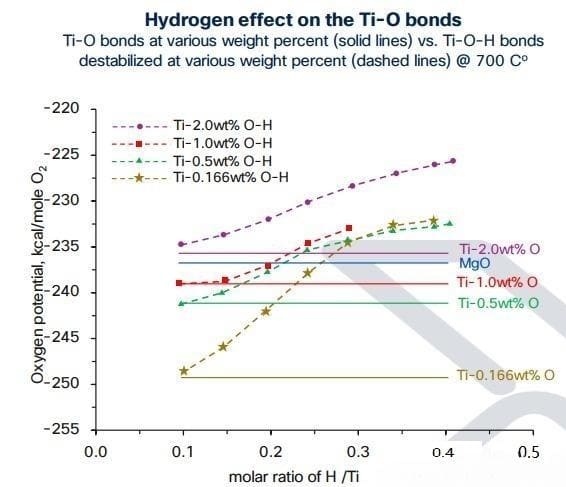
The low-cost manufacturing technology for titanium alloys is a hydrogen-assisted metal thermal reduction process, that employs titanium ore or scrap titanium alloy feedstocks to produce titanium powders with very low energy intensity, making it possible to achieve low-cost, low-carbon emission production in a sustainable closed loop. Hydrogen can destabilize Ti-O, and Mg reduction of TiO is used to achieve reductive deoxidation, forming TiH with low oxygen content to meet industrial needs, and then TiH is further processed into titanium metal by industry-standard methods.
3D Printed Titanium Powder Low-cost Manufacturing Technology
Based on the gas-solid two-phase flow theory, a new method for fluidized preparation of low-cost metal powder for 3D printing was established: using low-cost irregular-shaped powder (such as hydrogenated dehydrogenated titanium powder, reduced tungsten powder, etc.) prepared by traditional processes as raw materials, at an appropriate temperature, irregular-shaped powder particles (solids) collide with each other under the action of flowing gas (fluid), showing fluidization phenomenon, metallurgical bonding and plastic deformation between particles significantly improve the shape, sphericity, and flowability of irregular powder, and can achieve controllable powder flowability and impurities.
This process has the characteristics of short process, high yield, low energy consumption, and easy scalability. The fluidized powder has comparable performance to spherical powder, and the cost is more than 60% lower than atomized spherical powder. The 3D-printed products have excellent performance.
In the long run, additive manufacturing is more suitable for handling recycled materials than traditional manufacturing, simply because much less material is wasted at the start.
If the recycling capacity is not greatly and rapidly expanded, it seems impossible to achieve the goal of increasing the production scale and reducing carbon emissions of 3D printing. Waste powder recycling and remanufacturing is the type of application that 3D printing may receive more large-scale investment in the next few years.
Heeger Materials is a reputable supplier offering top-notch Titanium Alloy and Spherical Powder products at competitive prices, which are widely used in 3D printing industries. If you're interested, feel free to reach out to us at [email protected] for a quote, and we guarantee a response within 24 hours.


